November 12, 2025
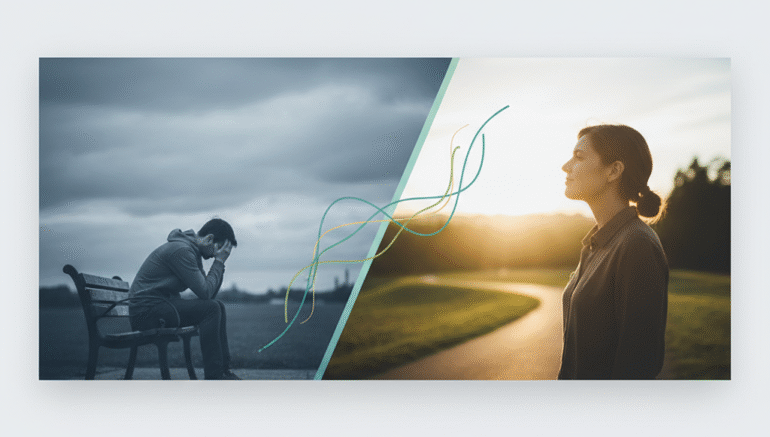
Stress and Depression have become a part of life in the modern, fast-paced world. The persistent emotional pain that disrupts work, relationships, and health may indicate depression or anxiety, although in some cases, occasional anxiety and sadness are normal. The two disorders are classified as the most prevalent mental health issues in the U.S., but a great number of individuals are reluctant to discuss them and seek assistance.
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) states that over 21 million adults in the United States have at least one major episode of depression every year, and approximately 40 million live with some type of anxiety disorder. The first step to healing is knowing what they entail and the ways of dealing with them.
What Does Depression and Anxiety Mean?
Every person has good days and bad days, though depression and anxiety are much more than temporary. They influence the manner in which an individual thinks, feels, and how he or she deals with the world.
Depression can be described as a dark fog of emotion, a sense of weight, numbing energy, and enthusiasm. All day-to-day activities might appear unachievable, and things that would have given pleasure before might not make sense.
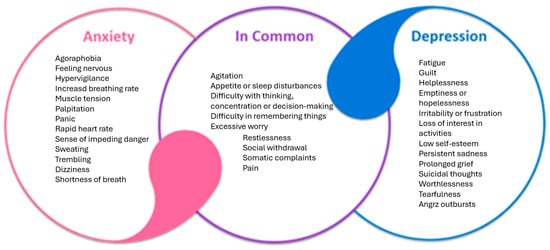
Anxiety, on the other hand, is a kind of alarm in your mind. You may be anxious, nervous, or suspicious without any apparent cause, worrying about matters that have not yet come to pass.
The conditions may either occur independently or in combination with each other, referred to as comorbid depression and anxiety, and thus tend to make symptoms more severe and more difficult to treat.
Depression and Anxiety Causes:
These mental illnesses do not have one cause. Rather, they are caused by a set of biological, psychological, and social factors.
- Genetics – It may be that in your family history, there is a history of depression or anxiety that can make you susceptible.
- Brain Chemistry Inequality in the neurotransmitters, like serotonin and dopamine, is a significant factor.
- Stressful Life Events– The symptoms may be instigated by loss, trauma, abuse, or economic hardship.
- Physical Health Conditions– they may include chronic illnesses, thyroid disorders, or hormonal disorders.
- Intake – Takes place of alcohol or drug abuse that may aggravate anxiety and depressive episodes.
Knowledge of such reasons can eliminate self-blaming. Mental illness is not an option- it is a health disorder that needs to be treated with sympathy and due care.
Understanding Depression and Anxiety
| Condition | What It Feels Like | Common Signs |
| Depression | A heavy emotional fog that drains motivation and joy. | Fatiguepoor focus,loss of interest,changes in sleep or appetite,feelings of guilt or hopelessness. |
| Anxiety | A constant sense of worry or restlessness that never seems to stop. | Racing thoughts,tension,irritability,sweating,sudden panic attacks. |
Treatment Options
The positive aspect is that depression and anxiety can be overcome. In the majority of cases, combination therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes relieve the majority of people.
1. Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy)
Therapy enables a person to realize what they think, feel, and behave like.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is the process focused on teaching how the negative styles of thought are to be replaced by healthier ones.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is concerned with emotional control and mindfulness.
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) enhances interpersonal relationships and communication.
2. Medication
Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can correct the balance of mood-related brain chemicals. Psychiatrists prescribe these and keep a close watch on their success.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Minor actions are capable of producing major results:
- Exercise can also be carried on regularly to release endorphins and ease stress.
- A balanced diet promotes psychological and physical health.
- Sleep is necessary to control mood.
- Anxiety can be reduced by mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
4. Support Networks
Friends, family, or peer support eases the process of recovery. Connection with other people who empathize with you helps to lessen the isolation and develop resilience.
5. Crisis Support
In case of an immediate danger to you or anyone you know, the assistance can be provided:
- 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline Call or text 988 (24/7).
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) Helpline: 1-800-950-NAMI (6264).
- SAMHSA treatment locator: Find local treatment at findtreatment.gov at an affordable cost..
The Community and Awareness Role.
It is important to eliminate the stigma of mental health to be able to recover. Free discussions make individuals express themselves by seeking assistance without embarrassment. There has been progress in community awareness programs, support groups, and school-based counseling programs, but more knowledge is required.
As communities discuss mental health openly, it will make some people less isolated and give them the strength to seek help. It is built by employers, educators, and families, among others, to create a culture of acceptance.
Living with Anxiety and Depression.
To recover does not imply that you always feel happy, but rather it is learning to cope with your feelings, to develop resilience and hope once more. The achievement of simple things such as getting out of bed, talking to a friend, or taking a walk is to be celebrated.
Conclusion
Depression and anxiety may overwhelm life, but they do not determine who you are. Recovery can definitely be achieved with the appropriate treatment, knowledge, and encouragement. The initial is the recognition that you have a right to feel good, and assistance can never be far away.
Make that first step today, whether it is to yourself or you know someone in need. Contact a counselor, communicate with a close one, or contact a mental health helpline. Healing starts with a single act, which is requesting someone to heal me.






